Introduction:
In our modern lives, electricity powers almost everything we do, from lighting our homes to running our gadgets. However, with the increasing number of devices we use daily, there’s a hidden danger lurking behind our walls: overloaded circuits. Understanding the signs of an overloaded circuit and knowing how to avoid hazards is crucial for ensuring safety in our homes and workplaces. For landlords, obtaining an EICR Certificate is essential to ensure electrical safety and compliance, making it a critical step in safeguarding properties against these risks.
What Causes Overloaded Circuits?
Before delving into the signs and hazards of overloaded circuits, it’s essential to understand what causes them. An overloaded circuit occurs when you plug in more electrical devices and appliances than the circuit can handle. This excess demand for electricity surpasses the capacity of the wiring and can lead to overheating, sparks, or even fire.
Several factors contribute to overloaded circuits:
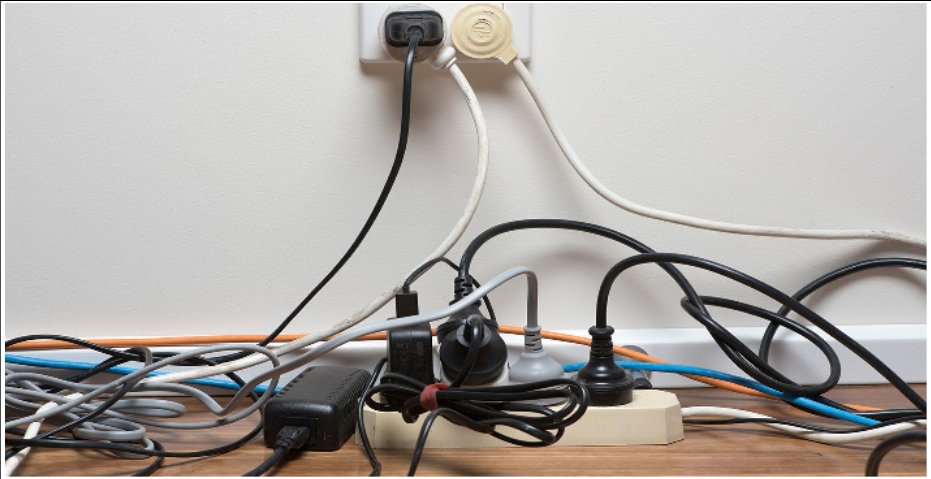
- Multiple Appliances: In households or workplaces where several appliances are plugged into a single outlet or circuit, there’s a higher risk of overloading. Common culprits include space heaters, air conditioners, refrigerators, and power strips.
- Old Wiring: Aging electrical systems may not be equipped to handle the electrical demands of modern technology. Outdated wiring, such as aluminum wiring or knob-and-tube systems, are particularly prone to overload and pose a significant safety risk.
- DIY Electrical Work: Incorrect wiring or DIY electrical installations can overload circuits. Amateur installations may not adhere to safety codes or load capacity guidelines, increasing the likelihood of electrical hazards.
- Extension Cords and Power Strips: While convenient, using too many extension cords or power strips can overload circuits. Plugging multiple high-wattage devices into a single power strip can quickly exceed its capacity and lead to overheating.
Recognizing the Signs of an Overloaded Circuit
Identifying the signs of an overloaded circuit is essential for preventing electrical hazards. Here are some common indicators to watch out for:
- Frequent Circuit Breaker Trips: If your circuit breaker frequently trips or fuses blow, it’s a sign that your electrical system is overloaded. Circuit breakers trip as a safety measure to prevent overheating and fires caused by excessive electrical current.
- Flickering Lights: When lights dim or flicker regularly, especially when you’re using appliances, it could indicate an overloaded circuit. Dimming lights suggest that the circuit is struggling to supply enough power to all connected devices simultaneously.
- Warm Outlets or Switches:Touching an outlet or switch and feeling warmth is a red flag for an overloaded circuit. Heat is a byproduct of excessive electrical current flowing through the wiring and can lead to melting insulation or even fire.
- Burning Smell: A persistent burning smell, especially near outlets or electrical panels, signals a potentially dangerous situation. It could indicate overheating wiring or components, which requires immediate attention to prevent a fire.
Preventing Hazards from Overloaded Circuits
Now that we’ve identified the signs of an overloaded circuit, let’s explore how to prevent hazards and ensure electrical safety:
- Limit Appliance Use: Be mindful of how many appliances you plug into a single outlet or circuit. Spread out the electrical load by using different circuits for high-wattage devices and avoid connecting multiple appliances to the same outlet.
- Upgrade Wiring: If you live in an older home with outdated wiring, consider upgrading to modern electrical systems. Consult a licensed electrician to assess your wiring’s condition and recommend necessary upgrades to handle today’s electrical demands safely.
- Use Power Strips Wisely: When using power strips or extension cords, choose ones with built-in overload protection and surge suppression. Avoid daisy-chaining power strips or plugging high-wattage appliances into them to prevent overloading.
- Unplug Unused Devices: Get into the habit of unplugging devices when they’re not in use, especially power-hungry appliances like space heaters or gaming consoles. Even in standby mode, electronic devices draw power and contribute to the overall electrical load.
- Schedule Electrical Inspections: Regular electrical inspections by a qualified electrician are essential for identifying potential hazards and ensuring your electrical system is up to code. Schedule inspections at least once every few years, or sooner if you notice any signs of electrical problems.
- Educate Family Members: Teach household members about the dangers of overloaded circuits and how to use electrical devices safely. Encourage everyone to report any signs of electrical problems promptly and avoid DIY electrical work unless they’re trained professionals.
Conclusion
Overloaded circuits pose a significant safety risk in homes and workplaces, but with awareness and preventive measures, these hazards can be mitigated. By recognizing the signs of an overloaded circuit and taking steps to alleviate the strain on your electrical system, you can protect your property and loved ones from electrical fires and other dangers. Prioritize electrical safety by practicing responsible energy usage and seeking professional assistance when needed, ensuring a secure and reliable power supply for years to come. For landlords, obtaining safety certificates from companies like Landlord Certification is a crucial step in maintaining electrical safety and compliance.If you want to stay updated with posts like this, please follow us on BLOGEBOIS.